PCB Assembly

PCB Assembly Steps
1. PCB Fabrication (Bare Board)
- PCB is manufactured from Gerber files
- Copper layers, solder mask, and silkscreen are applied
- Electrical testing of the bare board is done
Output: Empty PCB with pads, vias, and traces
2. Solder Paste Application
- Stainless steel stencil aligned with PCB
- Solder paste spread onto component pads
- Ensures correct solder volume
Used mainly for: SMT assembly


3. Component Placement (SMT)
- Pick-and-place machine mounts SMD components
- Components placed on solder paste
- High-speed and high-precision process
Components: Resistors, capacitors, ICs, BGAs, QFNs


4. Reflow Soldering
- PCB passes through temperature-controlled oven
- Solder paste melts and forms joints
- Components are permanently attached
Key control: Temperature profile
5. Through-Hole Component Insertion (THT)
- Leads inserted into drilled holes
- Can be manual or automated
- Used for connectors, transformers, large capacitors

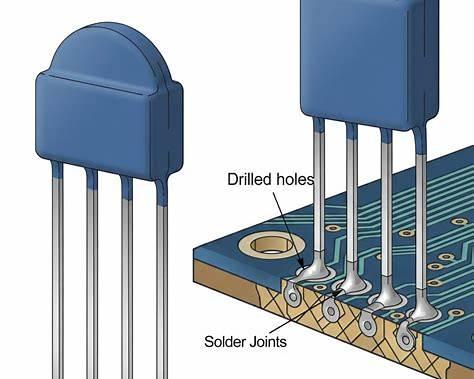
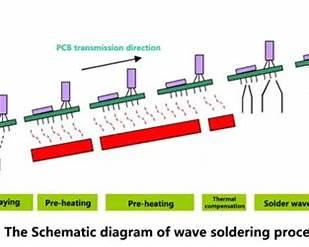
6. Wave / Hand Soldering (THT)
- Wave soldering for mass production
- Hand soldering for prototypes or repairs
- Solder bonds leads to pads


7. Inspection & Quality Control
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection)
- X-ray inspection for BGAs
- Visual inspection for solder defects
Checks for: Shorts, opens, misalignment


8. Electrical Testing
- In-Circuit Test (ICT)
- Functional Testing (FCT)
- Confirms circuit operates correctly


9. Cleaning & Final Assembly
- Flux residue removal
- Final visual inspection
- Preparation for coating or packaging
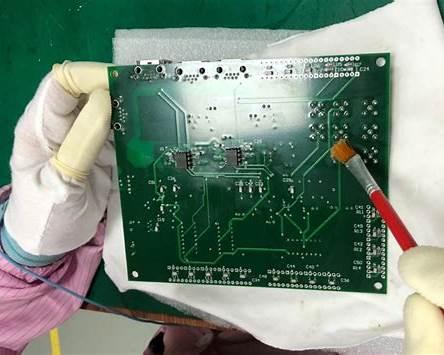
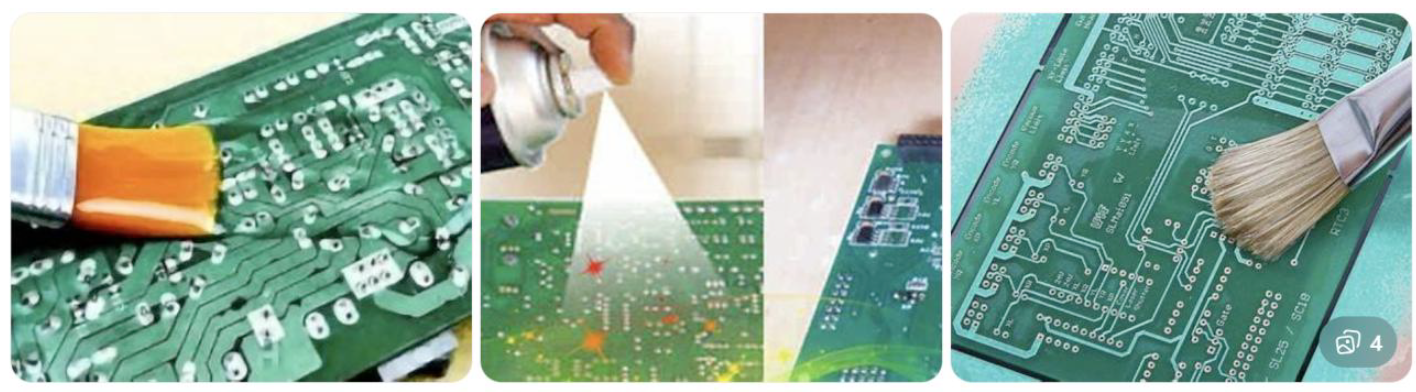
10. Conformal Coating
A thin, protective polymer layer applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) that “conforms” to components and traces, shielding them from moisture, dust, chemicals, and corrosion.
Why It’s Used
- Moisture & humidity protection
- Corrosion resistance (salts, pollutants)
- Prevents leakage & short circuits
- Improves reliability in harsh environments
- Extends product lifespan
Common Coating Types
| Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic (AR) | General electronics | Easy rework, fast dry | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Silicone (SR) | High temp, vibration | Flexible, wide temp range | Harder to remove |
| Urethane (UR) | Chemical exposure | Excellent chemical resistance | Difficult rework |
| Parylene (XY) | High-reliability | Ultra-thin, uniform | Expensive, special process |
Conformal Coating Machine (Automated / Selective)
Typical use: Medium–high volume production
Key features:
- Programmable XYZ motion
- Precise needle/spray valves
- Minimal masking required
- Consistent thickness & repeatability

Conformal Coating Hand Application (Manual)
Typical use: Prototypes, rework, low volume
Key features:
- Brush, aerosol spray, or syringe
- Low equipment cost
- Operator-dependent quality
Box Build PCB Assembly
What PCB Box Build Consists Of
- PCB mounted inside enclosure (metal or plastic)
- Wiring & cable harnesses (connectors, terminals)
- Mechanical assembly (standoffs, brackets, screws)
- Power supplies, switches, fans, displays (as required)
- Labels & grounding points